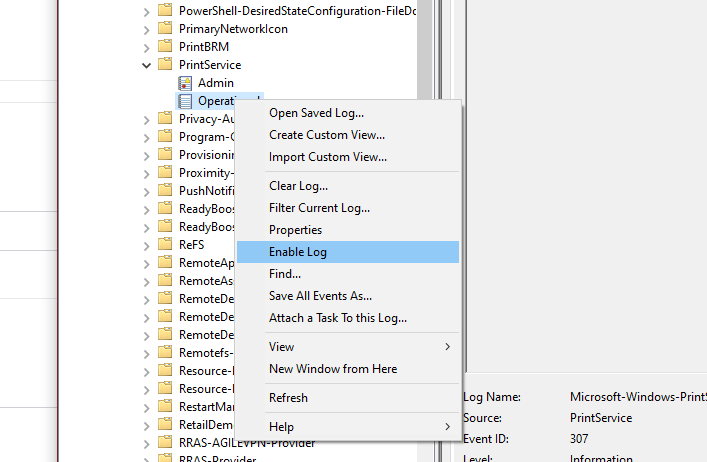
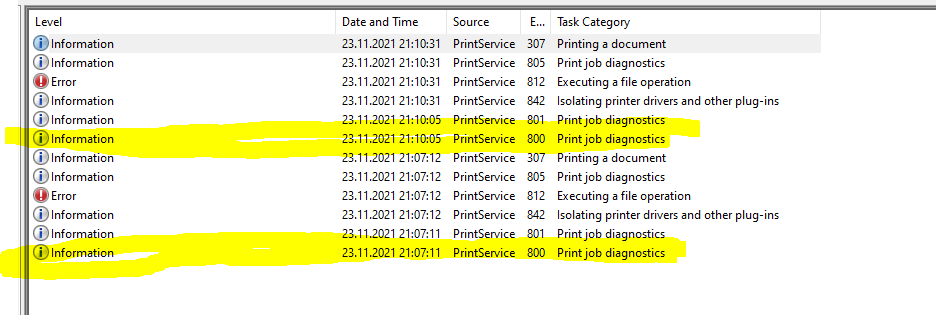
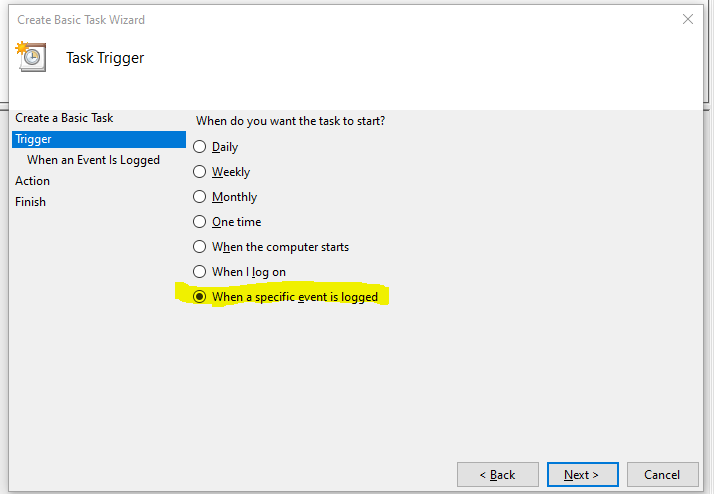
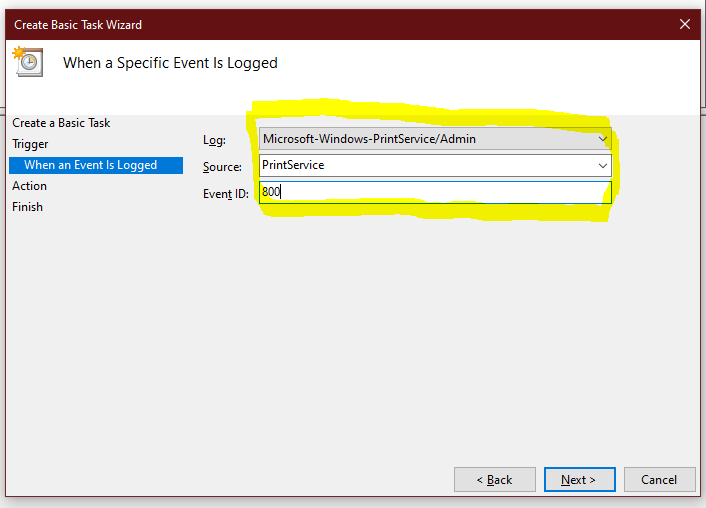
Just a simple script to test ESXi Connectivity and return the current license state of the server by using PowerCLI
param(
[Parameter(Mandatory = $true, HelpMessage = 'Provide username for login on ESXi')]
[String] $username,
[Parameter(Mandatory = $true, HelpMessage = 'Provide password for login on ESXi', ParameterSetName = 'Secret')]
[Security.SecureString] $password
)
#check user/pwd
if($username -like "" -Or $password -like "")
{
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Red "Username/Password seems wrong"
exit(1)
}
#define domain
$domain="forensik.justiz.gv.at"
#disable certificate checking as we have self signed certs
Set-PowerCLIConfiguration -InvalidCertificateAction Ignore -Confirm:$false
$hosts="SITE01-ESX01","SITE01-ESX02","SITE01-ESX03","SITE01-ESX04","SITE01-ESX05","SITE01-ESX06","SITE02-ESX01","SITE02-ESX02","SITE02-ESX03","SITE02-ESX04","SITE02-ESX05","SITE02-ESX06"
foreach($var_host in $hosts)
{
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Yellow $var_host"."$domain
Connect-VIServer -Server $var_host"."$domain -User $username -Password ([Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal]::PtrToStringAuto([Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal]::SecureStringToBSTR($password)))
$(Get-VMHost).Name
$(Get-VMHost).Version
$(Get-VMHost).LicenseKey
$(Get-VMHost).Uid
Disconnect-VIServer $var_host"."$domain -WarningAction SilentlyContinue -Confirm:$false
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Cyan "~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~"
}