While I was trying to update a VMware vCenter 6 to 6u1 today I had the problem, that the upgrade failed permanently, because of the following error:
Installation of component VMware JRE standalone installer failed with error code ‘3010’. Check the logs for more details.
Searching on the net did not bring up any results regarding this error, so I had to debug it myself. I tried to call the vmware-jre.msi directly from the DVD-ISO, and at first it seemd to run through, but, after some minutes of waiting, the MSI opened a pop up and asked for the installation-CD for vmware-jre.msi. It seemd that the new MSI wanted to uninstall the old msi-package and when trying to uninstall the old package the problem with the installation-media-dialoge popped up.
Trying to install the old version from the already installed vCenter also ended up in asking for an installation media.
At the end I started an administrative cmd-window and ran “msiexec /uninstall vmware-jre.msi” which uninstalled the old JRE and afterwards an update-process of the vCenter was possible.
Dump from the Error-Log:
[pastacode lang=”bash” message=”VMware JRE – Installation – Error log” highlight=”” provider=”manual”]
Stage: install stage: install-packages / vmware-jre.msi
2015-12-17 13:53:07.820Z| vcsInstUtil-3018519| I: LaunchPkgMgr: Telling child to install "X:\vCenter-Server\Packages\vmware-jre.msi" with "INSTALLPATH="C:\Program Files\VMware\vCenter Server\" VM_UPDATE=1" details 0
2015-12-17 13:53:07.820Z| vcsInstUtil-3018519| I: wWinMain: Exe is told to run "X:\vCenter-Server\Packages\vmware-jre.msi" with "INSTALLPATH="C:\Program Files\VMware\vCenter Server\" VM_UPDATE=1" details 0
2015-12-17 13:53:18.882Z| vcsInstUtil-3018519| E: wWinMain: MSI result of install of "X:\vCenter-Server\Packages\vmware-jre.msi" may have failed: 3010 (0x00000bc2)
2015-12-17 13:53:18.882Z| vcsInstUtil-3018519| E: LaunchPkgMgr: Operation on vmware-jre.msi appears to have failed: 3010 (0x00000bc2)
2015-12-17 13:53:18.882Z| vcsInstUtil-3018519| I: PitCA_MessageBox: Displaying message: "Installation of component VMware JRE standalone installer failed with error code '3010'. Check the logs for more details."
2015-12-17 13:59:25.191Z| vcsInstUtil-3018519| I: LaunchPkgMgr: Telling child to revert transaction
[/pastacode]
UPDATE:
The MSI-packages are located on the vCenter installation disk. The iso can be downloaded from: https://my.vmware.com/web/vmware/details?productId=491&downloadGroup=VC600U1 (VMware Account needed)
Once the ISO is downloaded it can be mounted/opened (eg. 7zip) and the MSI-Packages are located at: \vCenter-Server\Packages\
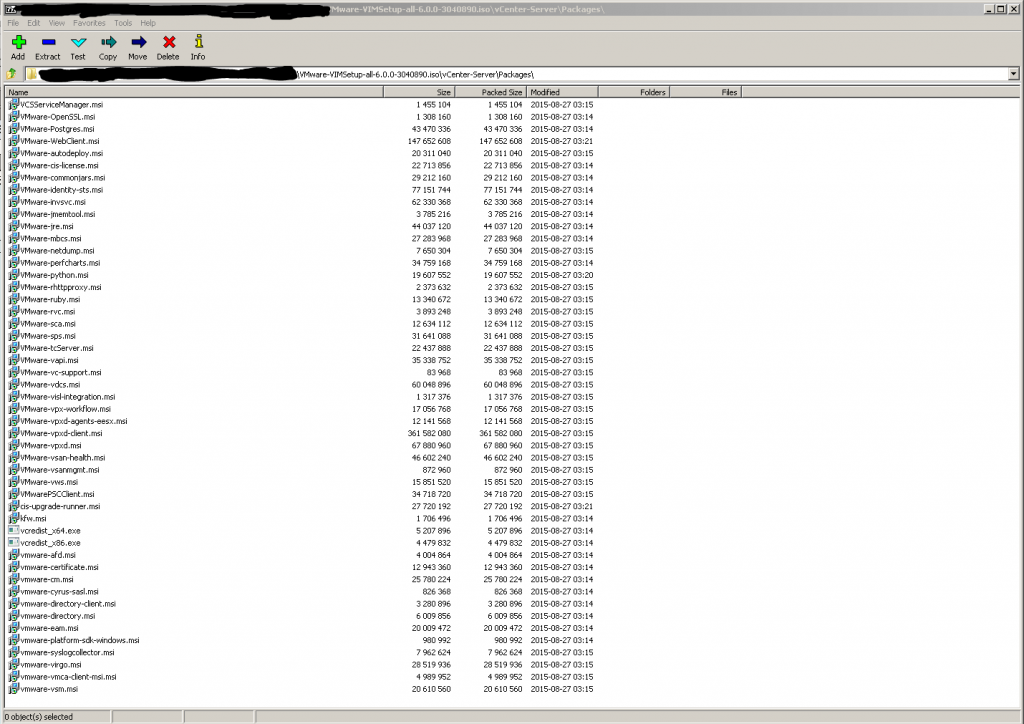
Mounting the ISO and chaning with an administrative commandline to the above path is the easiest way to uninstall the file. Otherwise the DVD-content could also be extracted to any directory.